A 4-step guide to exclude your own visits from Google Analytics 4.
 |
Why Should You Exclude Internal Traffic?
Clean data is better data, and better data leads to better decisions.
While there are several ways to generate cleaner data, excluding internal traffic from Google Analytics is an often neglected option.
Many companies configure their analytics systems to exclude internal user activity by filtering activity based on the user's IP address.
By omitting these users, analysts can concentrate solely on customer activities or other external users.
So if you visit your website more than once a day (I mean, who doesn't?), or have a large team that might do so, you should make sure to exclude their IP addresses so that you're getting clean data from GA4.
How to Exclude Your Visits from GA4?
These steps apply to Google Analytics 4.
If you're still using Universal Analytics, the process is a bit different.
Note that On July 1, 2023, Universal Analytics properties will cease data processing.
Step 1: Head to the "Admin" Section
- Sign in to your GA account
- Pick the property you want to apply the filter on
 |
- Click "Admin"
 |
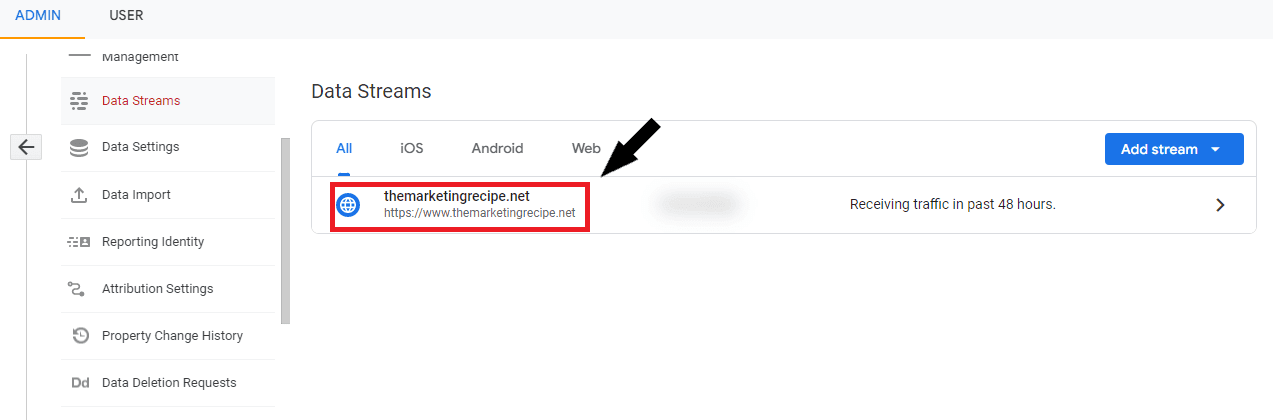
Step 2: Data Streams
Step 3: Define Internal Traffic
- Click "Show all"
 |
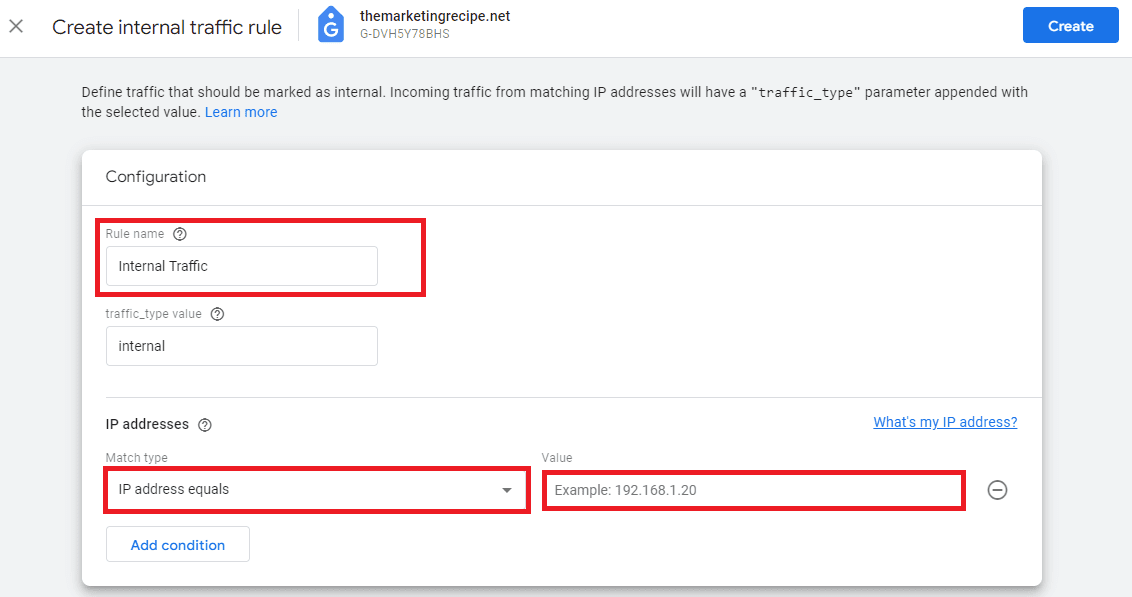
- Click "Define internal traffic"
- Click "Create"
- Name your rule
- traffic_type value: internal (default value)
- Select "IP address equals"
- Enter your IP address
 |
- Click "Create"
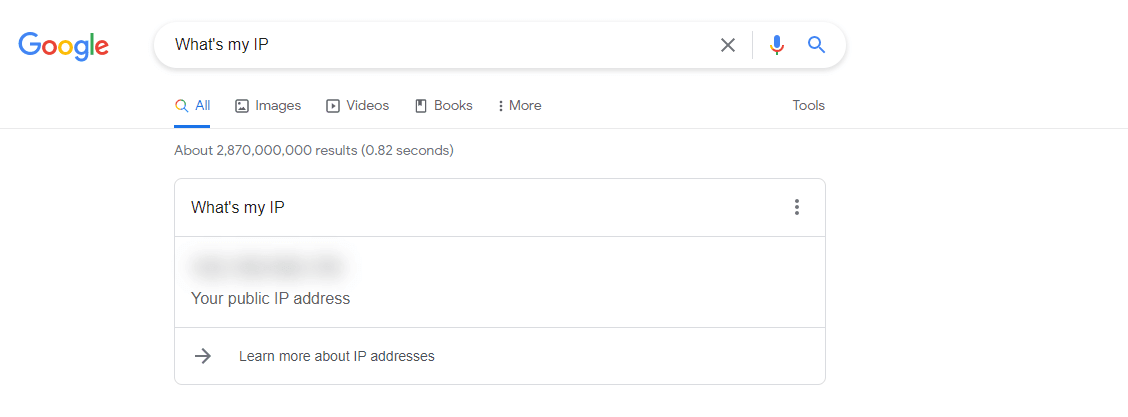
Where to Find Your IP Address?
To know your IP address, simply google: "What's my IP" and copy it.
 |
Step 4: Filter Internal Traffic
- Head back to the Admin panel
- Select "Data Settings"
- Click "Data Filters"
 |
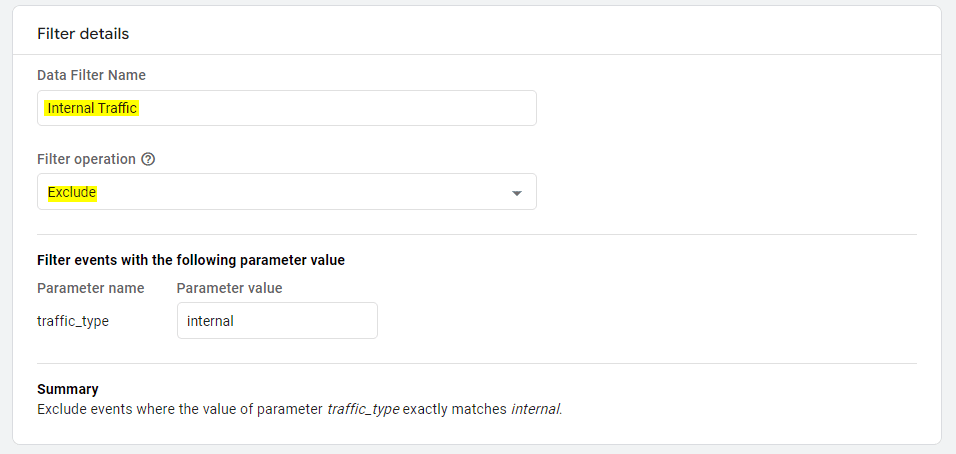
- Click "Create Filter"
- Select "Internal Traffic"
 |
- Name filter
 |
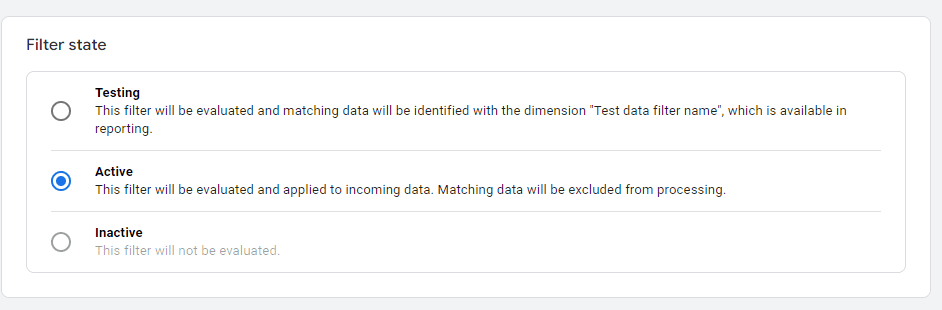
- Set the state to "Active"
 |
- Click "Create"
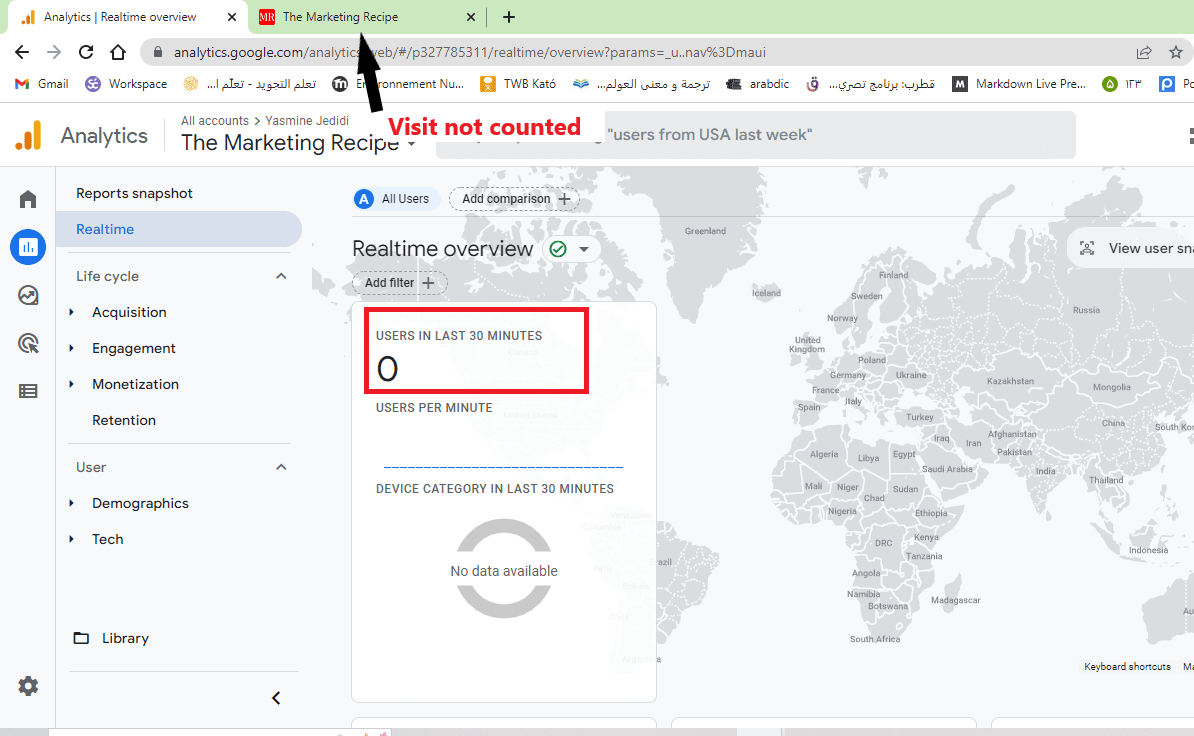
And that's it, your own visits won't be counted from now on.
Did you find this guide helpful? Let me know in a comment, I appreciate your feedback.
Tags
GA4